10 Unstoppable Companies with Dual Class Shares
Dual Class Shares: The Power of Control
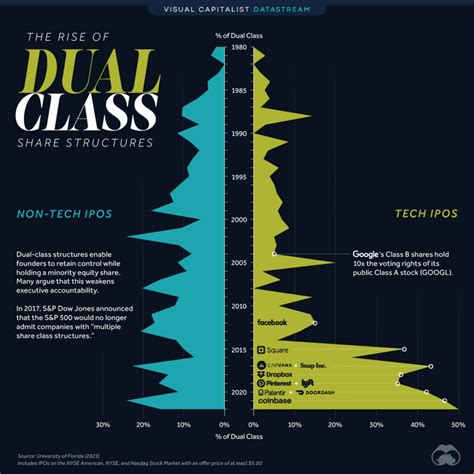
Dual class shares are a type of corporate structure that gives different classes of shareholders different levels of voting power. This can be used to give founders and early investors more control over a company, even if they do not own a majority of the shares.

There are many arguments for and against dual class shares. Proponents argue that they can help to protect founders’ vision for a company and allow them to make long-term decisions without being pressured by short-term investors. Opponents argue that dual class shares can lead to entrenchment and a lack of accountability, as founders and early investors may be able to control a company even if they no longer have the best interests of all shareholders at heart.
Despite the controversy, dual class shares remain a popular option for many companies. Here are 10 of the most notable companies with dual class shares:
- Alphabet (GOOGL)
- Berkshire Hathaway (BRK.A)
- Facebook (FB)
- Google (GOOG)
- Nike (NKE)
- Snap (SNAP)
- Spotify (SPOT)
- Tesla (TSLA)
- Under Armour (UAA)
- Visa (V)
These companies have all used dual class shares to give their founders and early investors more control over the company. In some cases, this has been used to protect the company’s culture and vision. In other cases, it has been used to entrench the founders in power.
The Pros and Cons of Dual Class Shares
There are a number of potential benefits to using dual class shares. These include:
- Protecting the founder’s vision: Dual class shares can help to protect the founder’s vision for a company by giving them more control over the company’s decision-making process. This can be important for companies that are trying to develop new products or technologies that may not be immediately profitable.
- Allowing for long-term decision-making: Dual class shares can also allow companies to make long-term decisions without being pressured by short-term investors. This can be important for companies that are trying to build a sustainable business over the long term.
- Reducing the cost of capital: Dual class shares can also reduce the cost of capital for companies. This is because investors are willing to pay a premium for companies with dual class shares, as they know that the founders and early investors will have a long-term commitment to the company.
However, there are also a number of potential risks associated with using dual class shares. These include:
- Entrenchment: Dual class shares can lead to entrenchment, as the founders and early investors may be able to control the company even if they no longer have the best interests of all shareholders at heart. This can lead to a lack of accountability and poor decision-making.
- Lack of accountability: Dual class shares can also lead to a lack of accountability, as the founders and early investors may not be held accountable for their decisions. This can lead to a lack of oversight and a lack of responsiveness to the needs of shareholders.
- Dilution of shareholder rights: Dual class shares can also lead to a dilution of shareholder rights, as the founders and early investors may have more voting power than other shareholders. This can make it difficult for other shareholders to have their voices heard and to hold the founders and early investors accountable.
The Future of Dual Class Shares
The future of dual class shares is uncertain. There is a growing movement to reform or eliminate dual class shares, as many investors believe that they are unfair and undemocratic. However, there are also many companies that believe that dual class shares are necessary to protect their founders’ vision and to allow them to make long-term decisions.
It is likely that the debate over dual class shares will continue for some time. However, it is clear that dual class shares are a powerful tool that can be used to give founders and early investors more control over a company. This can be used to protect the company’s culture and vision, to allow for long-term decision-making, and to reduce the cost of capital. However, it is important to be aware of the potential risks associated with dual class shares, including entrenchment, lack of accountability, and dilution of shareholder rights.