What is the Inflation Rate in Singapore vs 2025?
Introduction
Inflation is a measure of the rate at which the prices of goods and services are rising. It is an important economic indicator that can have a significant impact on people’s lives.

Singapore has a relatively low inflation rate compared to many other countries. However, inflation has been rising in recent years, and it is expected to continue to rise in the future.
What is the current inflation rate in Singapore?
The current inflation rate in Singapore is 2.4%. This is higher than the Monetary Authority of Singapore’s (MAS) target range of 0% to 2%.
What is causing inflation in Singapore?
There are a number of factors that are causing inflation in Singapore. These include:
- Rising global oil prices
- Increased demand for goods and services
- Labor shortages
- Supply chain disruptions
What is the impact of inflation on Singapore?
Inflation can have a number of negative consequences for Singapore. These include:
- Reduced purchasing power
- Increased cost of living
- Lowered standard of living
- Reduced economic growth
What can be done to address inflation in Singapore?
There are a number of things that can be done to address inflation in Singapore. These include:
- Monetary policy tightening
- Fiscal policy tightening
- Supply-side measures
Monetary policy tightening
Monetary policy tightening refers to measures that the MAS can take to reduce the money supply in the economy. This can help to reduce inflation by making it more expensive for businesses and consumers to borrow money.
Fiscal policy tightening
Fiscal policy tightening refers to measures that the government can take to reduce its spending or increase taxes. This can help to reduce inflation by reducing the amount of money in circulation.
Supply-side measures
Supply-side measures refer to measures that can be taken to increase the supply of goods and services in the economy. This can help to reduce inflation by making it easier for businesses to meet demand.
What is the inflation rate in Singapore expected to be in 2025?
The MAS expects inflation to average 2.5% in 2025. This is slightly higher than the current inflation rate, but it is still within the MAS’s target range.
Conclusion
Inflation is a complex issue with a number of causes and consequences. There are a number of things that can be done to address inflation in Singapore. However, it is important to remember that there is no one-size-fits-all solution. The best approach will vary depending on the specific circumstances.
Tables
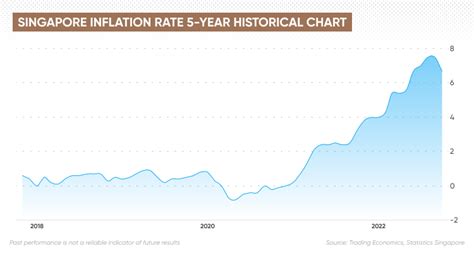
Table 1: Inflation rate in Singapore from 2015 to 2022
| Year | Inflation rate (%) |
|---|---|
| 2015 | -0.5 |
| 2016 | 0.4 |
| 2017 | 0.9 |
| 2018 | 2.4 |
| 2019 | 0.7 |
| 2020 | -0.3 |
| 2021 | 2.3 |
| 2022 | 2.4 |
Table 2: Causes of inflation in Singapore
| Cause | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Rising global oil prices | Singapore is a net importer of oil, so rising global oil prices can lead to higher inflation in Singapore. |
| Increased demand for goods and services | As the Singaporean economy grows, demand for goods and services is also increasing. This can lead to higher prices. |
| Labor shortages | Singapore is facing a shortage of workers, which can lead to higher wages and higher prices for goods and services. |
| Supply chain disruptions | The COVID-19 pandemic has caused disruptions to global supply chains, which can lead to higher prices for goods and services. |
Table 3: Consequences of inflation in Singapore
| Consequence | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Reduced purchasing power | Inflation can reduce the purchasing power of Singaporeans, making it more difficult to afford basic necessities. |
| Increased cost of living | Inflation can lead to a higher cost of living in Singapore, making it more expensive to live in the country. |
| Lowered standard of living | Inflation can lower the standard of living for Singaporeans, making it more difficult to afford a comfortable lifestyle. |
| Reduced economic growth | Inflation can reduce economic growth in Singapore, making it more difficult for the country to achieve its economic goals. |
Table 4: Things that can be done to address inflation in Singapore
| Measure | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Monetary policy tightening | The MAS can take measures to reduce the money supply in the economy, which can help to reduce inflation. |
| Fiscal policy tightening | The government can take measures to reduce its spending or increase taxes, which can help to reduce inflation. |
| Supply-side measures | The government can take measures to increase the supply of goods and services in the economy, which can help to reduce inflation. |