Exploring the Intricate Network: The Nervous System Made Easy
The human body is a marvel of complexity, with each system playing a vital role in our overall functioning. Among these systems, the nervous system stands out as the command center, coordinating communication throughout the body. In this article, we’ll embark on a fascinating journey through the nervous system, exploring its structure, functions, and the latest advancements in its study.

Understanding the Nervous System: A Vital Overview
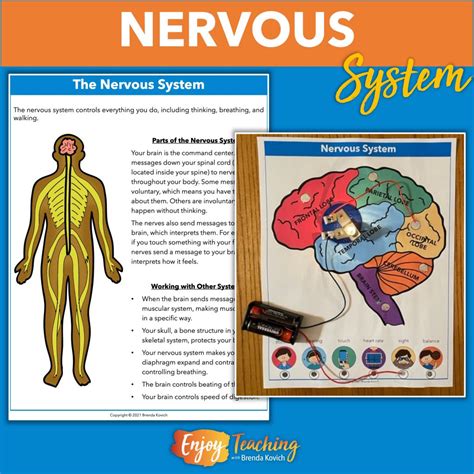
The nervous system is a vast, interconnected network of specialized cells called neurons. These neurons communicate with each other through electrical and chemical signals, relaying information from sensory receptors to muscles and organs throughout the body.
Key Functions of the Nervous System:
- Sensory Reception: Detects stimuli from the environment and internal organs.
- Information Processing: Analyzes and interprets sensory information.
- Motor Control: Generates signals to control muscle movement.
- Cognitive Functions: Supports higher-level functions such as memory, learning, and decision-making.
- Homeostasis: Regulates and maintains the body’s internal environment.
Structurally Speaking: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System
The nervous system is divided into two main divisions: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
Central Nervous System (CNS):
- Comprises the brain and spinal cord.
- Coordinates and controls the body’s activities.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS):
- Includes all nerves and sensory receptors outside the CNS.
- Connects the CNS to the rest of the body.
Unveiling the Central Nervous System: The Brain and Spinal Cord
The brain and spinal cord form the central command center of the nervous system.
The Brain:
- The brain is a complex organ that controls all aspects of the body’s functions.
- It is divided into three main parts: the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem.
- The cerebrum is responsible for higher-level functions such as cognition, language, and memory.
- The cerebellum coordinates muscle movement and balance.
- The brainstem controls vital functions such as breathing, heart rate, and sleep-wake cycles.
The Spinal Cord:
- The spinal cord is a long, cylindrical structure that extends from the base of the brain down the back.
- It transmits signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
Exploring the Peripheral Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Divisions
The PNS is further divided into two main subdivisions:
Sensory (Afferent) Division:
- Carries sensory information from the body to the CNS.
- Includes sensory receptors (e.g., touch receptors, pain receptors) and sensory nerves.
Motor (Efferent) Division:
- Transmits signals from the CNS to muscles and organs.
- Includes motor neurons and motor nerves.
Innovative Technologies Revolutionizing Nervous System Research
Advances in technology have revolutionized the study of the nervous system.
Electroencephalography (EEG):
- Measures electrical activity in the brain using electrodes placed on the scalp.
- Used to diagnose and monitor conditions such as epilepsy and sleep disorders.
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI):
- Visualizes changes in blood flow to different parts of the brain during activity.
- Used to study brain function in real-time.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS):
- Uses magnetic stimulation to temporarily disrupt or enhance brain activity.
- Used to treat conditions such as depression and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Clinical Significance: Conditions and Disorders of the Nervous System
Disorders of the nervous system can have a profound impact on our lives.
Neurological Disorders:
- Conditions that affect the structure or function of the brain or spinal cord.
- Include stroke, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis.
Psychiatric Disorders:
- Disorders that affect thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.
- Include depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder.
Common Mistakes to Avoid: Maintaining a Healthy Nervous System
Maintaining a healthy nervous system is essential for overall well-being. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol use can damage neurons and disrupt brain function.
- Smoking: Smoking deprives the brain of oxygen and nutrients.
- Poor Sleep: Lack of sleep can impair cognitive function and memory.
- Stress: Chronic stress can lead to anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues.
Expert Tips: Fostering a Thriving Nervous System
- Regular Exercise: Exercise increases blood flow to the brain and promotes neuron growth.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports brain health.
- Cognitive Stimulation: Engage in mentally stimulating activities such as reading, puzzles, and games.
- Stress Management: Learn and practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation and yoga.
Conclusion: The Marvelous Symphony of the Nervous System
The nervous system is a complex and dynamic network that plays a crucial role in every aspect of our being. By understanding its functions, structure, and the latest advancements in its study, we gain a deeper appreciation for the remarkable capabilities of this vital system. By maintaining a healthy nervous system through positive lifestyle choices, we can optimize our physical and mental well-being and unlock our full potential.
Table 1: Key Components of the Nervous System
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Neuron | Specialized cell that transmits electrical and chemical signals |
| Synapse | Junction between two neurons where signals are transmitted |
| Neurotransmitter | Chemical messenger that facilitates communication between neurons |
| Glial Cell | Non-neuronal cell that supports and protects neurons |
Table 2: Disorders of the Nervous System
| Condition | Type | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Stroke | Neurological | Sudden loss of blood flow to the brain |
| Alzheimer’s Disease | Neurological | Progressive loss of memory and cognitive function |
| Parkinson’s Disease | Neurological | Difficulty with movement, trembling, and rigidity |
| Multiple Sclerosis | Neurological | Damage to the myelin sheath that surrounds neurons |
| Depression | Psychiatric | Persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest |
Table 3: Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Nervous System
| Tip | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Regular Exercise | Increases blood flow and neuron growth |
| Healthy Diet | Provides essential nutrients for brain health |
| Cognitive Stimulation | Enhances brain function and memory |
| Stress Management | Reduces anxiety and improves mood |
Table 4: Common Mistakes to Avoid
| Mistake | Consequences |
|---|---|
| Excessive Alcohol Consumption | Neuronal damage and cognitive impairment |
| Smoking | Reduced oxygen and nutrient supply to the brain |
| Poor Sleep | Cognitive dysfunction and memory problems |
| Chronic Stress | Anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues |