n-Butane and Isobutane: A Versatile Pair for 2025 and Beyond
Introduction

n-Butane and isobutane, two closely related hydrocarbons, have emerged as indispensable components in various industries. Their unique properties and versatility make them ideal for a wide range of applications, from fuel to refrigerants and beyond. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the distinct characteristics, benefits, and potential future uses of these remarkable compounds.
Key Differences: n-Butane vs. Isobutane
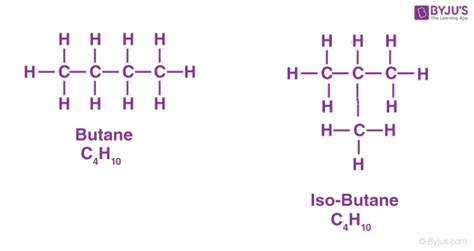
Structural Formula:
- n-Butane: CH3CH2CH2CH3
- Isobutane: (CH3)3CH
The primary difference between n-butane and isobutane lies in their structural formulas. n-Butane possesses a straight-chain structure, while isobutane has a branched structure.
Physical Properties:
| Property | n-Butane | Isobutane |
|---|---|---|
| Boiling Point (°C) | -0.5 | -10.2 |
| Melting Point (°C) | -138.3 | -159.6 |
| Density (g/mL) | 0.578 | 0.562 |
| Flammability | Highly flammable | Highly flammable |
Chemical Properties:
Both n-butane and isobutane are saturated hydrocarbons, meaning they exhibit low chemical reactivity. However, isobutane is slightly more reactive due to its branched structure.
Benefits of n-Butane and Isobutane
- Fuel: As a clean-burning fuel, n-butane is commonly used in lighters, camping stoves, and industrial applications. Isobutane has similar fuel properties and is often used as a primary or blended component in portable grills and gas cartridges.
- Refrigerants: n-Butane and isobutane are environmentally friendly refrigerants that are widely employed in household and commercial refrigeration systems. They have excellent thermodynamic properties and are considered safe and efficient alternatives to HCFCs and CFCs.
- Propellants: These hydrocarbons are used as propellants in various aerosol products, such as deodorants, hairsprays, and cleaning agents. Their low boiling points and high vapor pressures enable them to create a spray mist.
- Feedstocks: Both n-butane and isobutane serve as important feedstocks for the production of plastics, rubbers, and other chemical products.
Emerging Applications and Future Potential
The unique properties of n-butane and isobutane continue to inspire innovations and uncover new applications. Some promising areas of exploration include:
- Alternative Fuels: As the demand for sustainable energy sources grows, n-butane and isobutane are being investigated as potential biofuels or blends with gasoline.
- Propellants for Medical Applications: Isobutane’s low toxicity and non-flammability properties make it an attractive choice as a propellant for medical aerosols, such as inhalers and nebulizers.
- Refrigerants in Green Cooling Systems: The search for environmentally friendly cooling technologies has led researchers to explore the use of n-butane and isobutane as refrigerants in innovative heat pumps and air conditioning systems.
- New Polymers and Materials: The unique molecular structures of these hydrocarbons have the potential to yield novel polymers with enhanced properties for applications in engineering, electronics, and biomaterials.
Strategies for Enhancing Application
To fully realize the potential of n-butane and isobutane, several key strategies can be adopted:
- Research and Development: Continued investment in research and development is crucial to uncover new applications and optimize their performance.
- Collaboration: Fostering collaborations between industry, academia, and government can accelerate innovation and bring new products and technologies to market.
- Environmental Sustainability: Ensuring the sustainable production