Oxidation State of Oxygen in K₂O: An In-Depth Exploration
Understanding Oxidation States: A Key Concept
The oxidation state, also known as the oxidation number, is a crucial concept in chemistry that represents the hypothetical charge of an atom in a molecule or ion. It provides insights into the chemical behavior and reactivity of elements.

Oxidation State of Oxygen: A Versatile Element
Oxygen holds a prominent position in chemistry due to its remarkable ability to form compounds with a wide range of other elements. Its oxidation state varies significantly depending on the compound it forms.
Oxidation State of Oxygen in K₂O: -2
In the ionic compound potassium oxide (K₂O), oxygen exhibits an oxidation state of -2. This indicates that each oxygen atom has gained two electrons.
Properties of K₂O
K₂O is a white, crystalline solid with a high melting point (832°C) and a low boiling point (900°C). It is a highly reactive compound that readily absorbs moisture from the air. K₂O is also a powerful base that reacts with acids to form salts.
Applications of K₂O
The industrial applications of K₂O are extensive, including:
- As a fertilizer in agriculture to enrich soil with potassium
- In the production of glass, ceramics, and cement
- As an additive in detergent powders
- In the refining of petroleum and the production of chemicals
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When determining the oxidation state of oxygen in compounds, it is essential to avoid common mistakes such as:
- Assuming oxygen always has an oxidation state of -2: Oxygen’s oxidation state can vary significantly depending on the compound.
- Ignoring the overall charge of the molecule or ion: The oxidation states of all atoms must add up to the total charge of the species.
- Using incorrect rules for determining oxidation states: Specific rules apply for different types of compounds.
Step-by-Step Approach to Finding Oxidation States
To accurately determine the oxidation state of oxygen in K₂O, follow these steps:
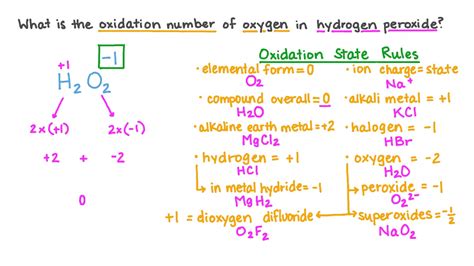
- Identify the oxidation state of the other element(s) in the compound. In K₂O, potassium has an oxidation state of +1.
- Determine the overall charge of the compound. K₂O is a neutral compound, so its overall charge is 0.
- Use the equation: Total oxidation state = 0 to solve for the oxidation state of oxygen.
(+1) + (x) = 0, where x represents the oxidation state of oxygen.
Solving for x, we get x = -2.
Therefore, the oxidation state of oxygen in K₂O is -2.
FAQs
Q1. Why is the oxidation state of oxygen in K₂O different from that in other compounds?
A1. The oxidation state of oxygen varies depending on the electronegativity of the other elements present in the compound. In K₂O, potassium is less electronegative than oxygen, resulting in an oxidation state of -2 for oxygen.
Q2. What is the significance of the negative oxidation state of oxygen in K₂O?
A2. The negative oxidation state indicates that oxygen has gained electrons and is in an anionic state. This allows it to react with positively charged ions to form ionic compounds.
Q3. Are there any safety precautions to consider when handling K₂O?
A3. Yes, K₂O is a reactive compound that can be corrosive. It is essential to handle it with caution, wear appropriate protective gear, and avoid direct contact with eyes, skin, and clothing.
Q4. What are the potential new applications for K₂O that are currently being explored?
A4. Researchers are investigating novel applications for K₂O in energy storage devices, nanomaterials, and biotechnology. Its unique properties, such as high reactivity and ability to form complex compounds, offer promising opportunities for innovation.
Table 1. Oxidation States of Oxygen in Common Compounds
| Compound | Oxidation State of Oxygen |
|---|---|
| H₂O | -2 |
| CO₂ | -2 |
| SiO₂ | -2 |
| Na₂O | -2 |
| CaO | -2 |
Table 2. Physical Properties of K₂O
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Appearance | White, crystalline solid |
| Melting point | 832°C |
| Boiling point | 900°C |
| Density | 2.32 g/cm³ |
| Solubility in water | Reacts to form KOH |
Table 3. Applications of K₂O by Industry
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Agriculture | Fertilizer |
| Construction | Glass, ceramics, cement |
| Household | Detergent powders |
| Petrochemical | Refining, chemical production |
Table 4. Safety Precautions for Handling K₂O
| Precaution | Reason |
|---|---|
| Wear gloves and safety glasses | Protects against skin and eye irritation |
| Handle in a well-ventilated area | Prevents inhalation of fumes |
| Avoid direct contact with skin and clothing | Causes burns and irritation |
| Store in a cool, dry place | Prevents decomposition |