Secured vs. Unsecured Bonds: A Detailed Comparison for 2025
Introduction

Bonds, foundational pillars of the financial landscape, come in two primary categories: secured and unsecured. Understanding the fundamental differences between these bond types is paramount for investors seeking to navigate the complexities of fixed income markets. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of secured and unsecured bonds, empowering investors with the knowledge to make informed investment decisions in 2025 and beyond.
Primary Keyword: Secured vs. Unsecured Bonds
Secondary Keywords: Fixed income, investment, 2025, secured, unsecured
1. Definition and Characteristics
# Secured Bonds
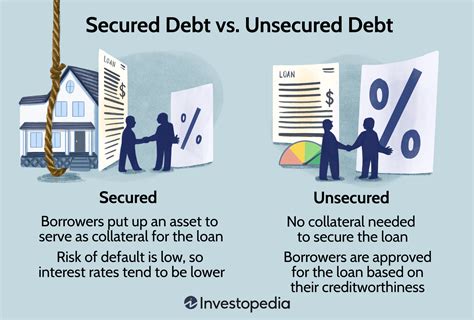
Secured bonds are financial instruments backed by collateral. In the event of a default, investors have a claim on the underlying asset serving as security.
Key Characteristics:
– Backed by collateral (e.g., real estate, equipment)
– Higher credit ratings
– Lower interest rates
– Priority repayment in case of default
# Unsecured Bonds
Unsecured bonds lack collateral, relying solely on the creditworthiness of the issuer. Thus, they carry higher risk compared to secured bonds.
Key Characteristics:
– Not backed by collateral
– Lower credit ratings
– Higher interest rates
– Subordinate repayment in case of default
2. Credit Risk and Ratings
# Credit Risk
Credit risk refers to the potential that an issuer will default on its bond payments. Secured bonds typically carry lower credit risk as collateral enhances the investor’s claim on assets. Unsecured bonds, lacking collateral, face higher credit risk.
# Credit Ratings
Credit ratings, assigned by independent agencies, reflect the issuer’s ability to repay its obligations. Secured bonds generally receive higher credit ratings due to the underlying collateral. Conversely, unsecured bonds often bear lower ratings because of their higher credit risk.
3. Interest Rates and Yields
# Interest Rates
Interest rates on secured bonds tend to be lower than those on unsecured bonds. This is because investors demand a premium for taking on higher credit risk associated with unsecured bonds.
# Yields
Yields, the annual percentage return on a bond, are inversely proportional to interest rates. As a result, secured bonds typically offer lower yields than unsecured bonds.
4. Seniority and Repayment**
# Seniority
In a default scenario, secured bondholders have priority over unsecured bondholders in terms of repayment. The collateral backing secured bonds ensures a higher likelihood of recovery in case of default.
# Repayment
Unsecured bondholders are subordinate to secured bondholders when it comes to repayment. In the event of liquidation, secured bondholders receive their principal and interest payments before unsecured bondholders.
5. Investment Considerations
# Investment Considerations for Secured Bonds
– Investors seeking lower risk and stable returns may prefer secured bonds.
– Collateralized assets provide additional protection against default.
– Higher credit ratings typically translate into lower interest rates and yields.
# Investment Considerations for Unsecured Bonds
– Investors seeking higher potential returns may consider unsecured bonds.
– Unsecured bonds offer higher yields due to their higher credit risk.
– Thorough research on issuer creditworthiness is crucial before investing in unsecured bonds.
6. Historical Performance and Market Trends
# Historical Performance
Secured bonds have historically performed better than unsecured bonds during periods of economic downturns. The presence of collateral provides a buffer against defaults, leading to more stable returns.
# Market Trends
In recent years, demand for secured bonds has increased as investors seek refuge from market volatility. As a result, yields on secured bonds have compressed, while yields on unsecured bonds have risen.
7. Case Study: Secured vs. Unsecured Bonds in Action
# Case Study: Company X
Company X issued both secured and unsecured bonds in 2023. The secured bonds were backed by company assets, while the unsecured bonds lacked collateral. The credit ratings for the secured bonds were higher than those for the unsecured bonds.
# Results
During the market downturn of 2024, Company X was unable to make its bond payments. As a result, secured bondholders were able to recover most of their principal and interest. However, unsecured bondholders experienced significant losses as their claims were subordinated to the secured bondholders.
This case study demonstrates the importance of considering credit risk and collateralization when investing in bonds. Secured bonds provide a greater level of protection against default and loss.
8. FAQs
# Frequently Asked Questions
– What is the key difference between secured and unsecured bonds?
– Secured bonds are backed by collateral, while unsecured bonds are not.
– Which type of bond is less risky?
– Secured bonds are generally less risky due to the presence of collateral.
– Which type of bond pays a higher interest rate?
– Unsecured bonds typically offer higher yields because of their higher credit risk.
– Who has priority in repayment in case of default?
– Secured bondholders have priority over unsecured bondholders in terms of repayment.
– How do I choose between secured and unsecured bonds?
– Consider your risk tolerance, investment goals, and the issuer’s creditworthiness.
9. Innovatative Ideas for Bond Investors
# Creative New Word: Bondfusion
# Innovatative Idea: Bondfusion
Bondfusion is a novel concept that combines elements of both secured and unsecured bonds. Bondfusion involves creating a hybrid bond that offers the benefits of both bond types.
# Potential Benefits of Bondfusion
– Lower risk than unsecured bonds
– Higher returns than secured bonds
– Provides investors with a unique blend of credit protection and yield potential
Conclusion
Secured and unsecured bonds offer a spectrum of investment opportunities, each with unique risks and rewards. By understanding the fundamental differences between these bond types, investors can make informed decisions aligned with their financial objectives and risk tolerance. Whether seeking stability and protection or higher potential returns, bonds remain an integral component of any diversified portfolio.